HCOOCH CH2 H2O: Formula, Uses, and Key Reactions
Chemistry often brings us across unusual notations and shorthand references, especially when browsing scientific blogs, online study guides, or Q&A platforms. One such example is “HCOOCH CH2 H2O”. While this may look confusing at first glance, most reliable sources agree it points toward methyl formate (HCOOCH₃) and its interaction with water (H₂O), especially through hydrolysis.
This article will unpack the topic in detail, covering:
-
The correct chemical formula of methyl formate.
-
How “HCOOCH CH2 H2O” is interpreted in chemistry writing.
-
Key reactions involving methyl formate and water.
-
Industrial and laboratory uses of the compound.
-
Safety, environmental relevance, and practical applications.
By the end, you will have a clear picture of what the formula means, how the reactions proceed, and why this chemical is important both scientifically and industrially.
Breaking Down the Formula
What does “HCOOCH CH2 H2O” mean?
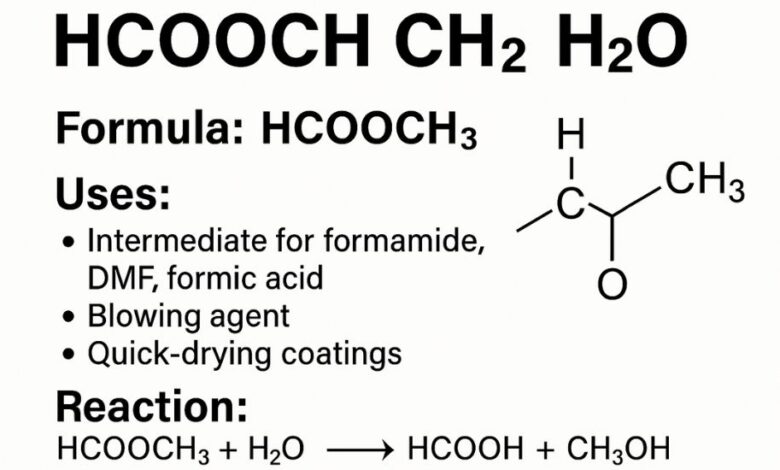
The notation itself is not a recognized IUPAC-standard chemical formula. Instead, it is shorthand often used in simplified explanations. When bloggers or learning platforms write HCOOCH CH2 H2O, they are typically referring to methyl formate (HCOOCH₃) in the context of its interaction with water.
-
Methyl formate formula: HCOOCH₃ (also written as C₂H₄O₂).
-
Molecular mass: ~60.05 g/mol.
-
Structure: It is the methyl ester of formic acid, containing a formate group (HCOO–) bonded to a methyl group (–CH₃).
Simplifying the interpretation
In practical terms:
-
HCOOCH₃ = methyl formate.
-
+ H₂O = hydrolysis or esterification context.
So “HCOOCH CH2 H2O” is best interpreted as a way of pointing to the reaction of methyl formate with water, which we’ll explore below.
The Chemical Formula in Detail
Structural formula
The structural representation of methyl formate is:
This illustrates the ester bond between the formyl group (HCOO–) and the methyl group.
Properties
-
Appearance: Colorless liquid.
-
Odor: Ether-like, with hints of alcohol.
-
Boiling point: ~32 °C (close to room temperature).
-
Water solubility: ~30% at 20 °C – partial solubility that enables easy hydrolysis.
-
Vapor pressure: High, meaning it evaporates quickly.
These properties explain its practical roles as a fast-evaporating solvent and a blowing agent in foams.
The Reaction with Water
Hydrolysis of methyl formate
The most important reaction is hydrolysis, where methyl formate reacts with water:
Equation:
HCOOCH₃ + H₂O → HCOOH + CH₃OH
-
Reactants: Methyl formate and water.
-
Products: Formic acid (HCOOH) and methanol (CH₃OH).
This is a classic ester hydrolysis reaction, typically requiring acidic or basic catalysis.
Mechanism (simplified)
-
The ester oxygen is protonated (in acid-catalyzed conditions).
-
Water attacks the carbonyl carbon, forming a tetrahedral intermediate.
-
The bond rearranges, releasing methanol and regenerating the catalyst.
Reverse reaction (esterification)
The hydrolysis reaction is reversible. Under different conditions:
Formic acid (HCOOH) + Methanol (CH₃OH) ⇌ Methyl formate (HCOOCH₃) + H₂O
This equilibrium is a textbook example of Fischer esterification.
Uses of Methyl Formate (HCOOCH₃)
Industrial intermediate
Methyl formate plays a critical role as a chemical feedstock, particularly for:
-
Formamide production → precursor for pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and resins.
-
Dimethylformamide (DMF) → widely used as a solvent in electronics, textiles, and chemical industries.
-
Formic acid synthesis → important for leather processing, rubber production, and as a preservative.
Solvent and processing aid
-
Used in quick-drying finishes (paints, coatings, and lacquers).
-
Sometimes used as a specialty solvent in extractions and reactions due to its volatility.
Blowing agent in foams
-
Employed in polyurethane foams as a low-GWP, non-ozone-depleting blowing agent.
-
Replaces CFCs, HCFCs, and HFCs in environmentally conscious manufacturing.
Other applications
-
Can be used in fumigants and pesticides (historically, though less common now due to safety concerns).
-
Investigated in niche fuel applications, as it burns cleanly compared to heavier hydrocarbons.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Safety hazards
-
Flammability: Highly flammable, with a flash point below room temperature.
-
Inhalation risks: Vapors can cause dizziness, irritation, and central nervous system effects.
-
Handling: Requires good ventilation, protective equipment, and proper storage away from heat sources.
Environmental impact
-
Ozone depletion potential (ODP): ~0 (environmentally safer than CFCs).
-
Global warming potential (GWP): Very low, making it a good choice for foam blowing.
-
Biodegradability: Breaks down relatively quickly compared to chlorinated solvents.
Academic and Practical Relevance
Methyl formate’s hydrolysis is often used in chemistry education to demonstrate ester reactions, catalysis, and reaction equilibria. At the same time, industries rely on it as a building block chemical, highlighting the bridge between theory and practice.
Conclusion
The term “HCOOCH CH2 H2O” may not be a standard formula, but it provides a window into one of the most important ester compounds: methyl formate. With the correct formula HCOOCH₃ (C₂H₄O₂), it serves as a vital chemical intermediate, a solvent, and an environmentally friendly blowing agent. Its hydrolysis to formic acid and methanol is a reaction of both industrial and educational importance.
Whether you are studying basic ester chemistry or looking at large-scale industrial processes, understanding this compound’s formula, uses, and reactions is key.
For more science-focused articles like this, visit Blog Loom — your source for detailed explanations and easy-to-read deep dives into the world of chemistry and beyond.


